Search Results for: y chromatin
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Y chromatin
y chromatin Brilliantly fluorescent body seen in cells stained with the dye quinacrine which lights up the y chromosomes... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Euchromatin
Definition noun A slightly packed or partially condensed form of chromatin that contains structural genes and is usually... Read More
Heterochromatin
Definition noun Highly condensed, tightly packed form of chromatin, as opposed to the lightly packed... Read More
Nuclear body
Definition noun plural: nuclear bodies nu·cle·ar bod‧y, ˈnjuː.kli.ər ˈbɒdi Any of the prominent non-membraned,... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
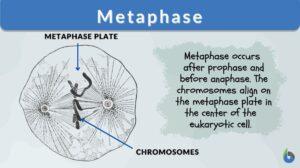
Prometaphase
Definition noun The phase of mitosis between prophase and metaphase wherein the nuclear envelope breaks down and form... Read More
Nuclear matrix
Definition noun plural: nuclear matrices (cell biology) A 3-dimensional filamentous protein network that extends... Read More
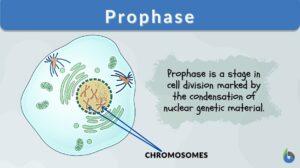
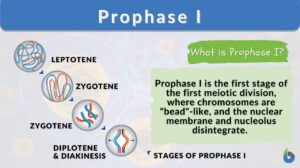
Prophase I
Organisms all use mitosis to create more cells in the body. Meiosis, a similar process, is used in some organisms to undergo... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Constitutive heterochromatin
Definition noun Regions on chromosomes that are condensed permanently, genetically inactive, and always in the same position... Read More
Facultative heterochromatin
Definition noun Heterochromatin that may lose its condensed state and becomes genetically active Supplement Heterochromatin... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Chromatin body
Chromatin body barr body, condensed x chromosome in female mammalian... Read More
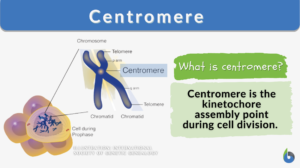
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
Nuclear lamina
Definition noun plural: nuclear laminae or nuclear laminas nu·cle·ar lam·i·na, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈlæm.ɪ.nə (cell... Read More
Constitutive heterochromatin banding
Definition noun (cytogenetics) A selective banding technique wherein a banding pattern is produced in the constitutive... Read More
Cells know when to separate at mitosis
How do cells know when to separate during mitosis? A molecule called BubR1 was found to regulate the timing of the division... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Recombination DNA repair
Recombination DNA Repair Definition Recombination DNA repair is a biological reparative process in response to DNA damage... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Chloroplast DNA
Definition noun plural: chloroplast DNAs DNA in the chloroplast that carries the code for proteins and RNAs essential to... Read More
Entamoeba histolytica
Definition noun A disease-causing anaerobic protozoan species capable of causing entamoebiasis and amebic dysentery to its... Read More
Prophase II
Definition noun The first stage in meiosis II highlighted by the disintegration of nucleolus and nuclear envelope, the... Read More
Linker DNA
Definition noun, plural: linker DNAs DNA linking adjacent nucleosome core particles Supplement A linker DNAs is a stretch of... Read More